Robot Cybersecurity Challenges with Remote Control Technologies
Robot cybersecurity is increasingly becoming a hot topic for manufacturers worldwide. Many businesses across different industries continue to automate production with robots to stave off the impacts of never-ending labor shortages. They have also started to leverage the Internet of Things (IoT) solutions to boost operational efficiency and resource management.
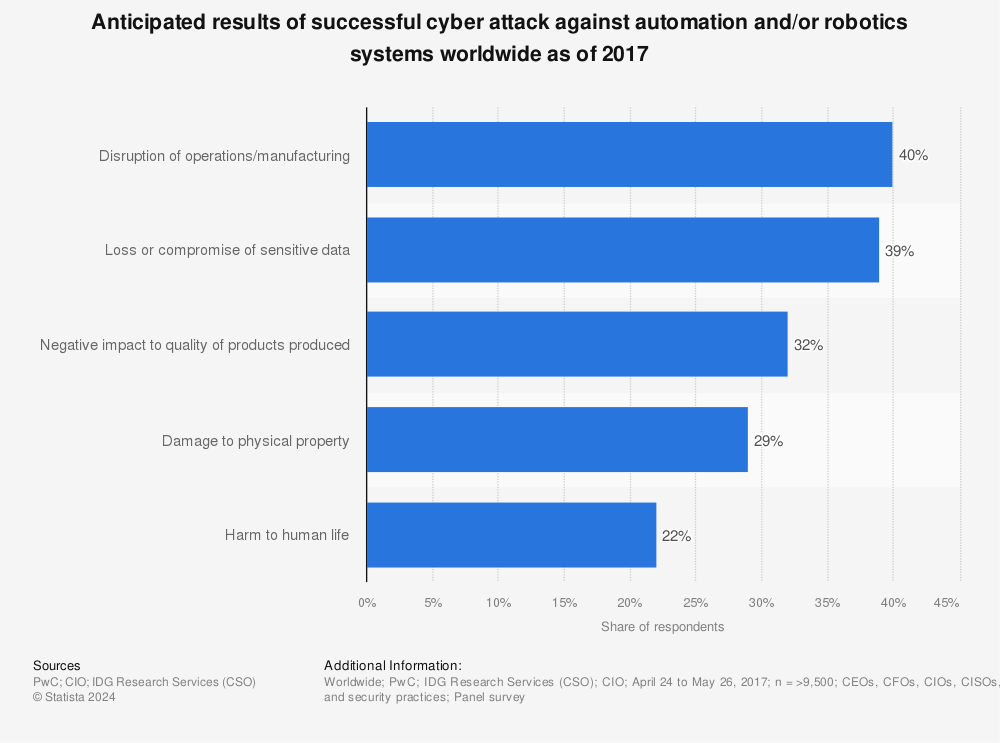
However, cyberattacks are inevitably on the rise. Connected manufacturing environments can be extremely vulnerable, leaving them open to hackers who can steal data, remotely control robots’ movements, and cause irreparable harm.
However, new approaches to robot cybersecurity are proving to be robust in protecting manufacturers from cyberthreats. According to some estimates, sales in the global robot cybersecurity market are set to reach USD $7.2 billion by 2029, growing at a CAGR of 11%.
Let’s take a look at the importance of robot cybersecurity, the challenges companies face, and potential solutions to mitigate cyberattacks to robotic systems.
Why Does Cybersecurity Matter in Robotics Nowadays?
Over the past decade, sales of industrial robots have boomed as more manufacturers make the transition to Industry 4.0 and operate smart, connected factories. According to the International Federation of Robotics (IFR), the annual installation of robots is expected to increase by 6% per annum over the next few years.
The advantages of industrial robots and cobots are undeniable. From increased output and efficiency to substantial cost savings from labor and operational standpoint, robots can be game changers for companies looking to gain a competitive edge.
In addition, combining robotics systems with remote access technologies enables teams to control equipment optimally and in real-time to reduce downtimes, accelerate maintenance, and optimize production even further, especially across multiple sites. It’s an entirely new manufacturing frontier that offers tremendous opportunities for forward-thinking organizations.
However, despite the fact that industrial robots and cobots appear to be a panacea for businesses across the board, industrial robot cybersecurity fears are surging.
The reason? Robotics systems are inherently complex, particularly when connected to cloud services to offload computational tasks or interact with other equipment and devices.
In a recent paper on cybersecurity, safety, and robots, researchers indicated that this complex robotic infrastructure can become extremely ripe for cybersecurity threats:
“The more functions are performed across interconnected systems and devices, the more opportunities for weaknesses in those systems to arise, and the higher the risk of system failures or malicious attacks.”
According to several industry pundits, robotics manufacturers focused primarily on the physical safety of human operators and their “interfacing” with robot systems. Robot cyber security was initially not top of mind. Nevertheless, as robotics systems become more interconnected and sophisticated, they also “unlock broader attack surfaces,” experts argue. Attack surfaces include the physical robot, operating system, software/firmware, remote control technologies, vendor Internet services, cloud services, and networks.
Robot cybersecurity vulnerabilities and a lack of modern robotics cybersecurity strategies have led to a proliferation of cyber threats. The motives hackers have to attack industrial robots, and cobots are numerous, such as:
Sabotaging robots to altercate parts or assemblies that are produced (adding faults or small defects)
Ransomware threats, whereby the hackers demand hefty ransoms to inform manufacturers what lots are impacted by production sabotage
Physically damaging the robot or robotic cell itself to harm workers
Stealing critical information/intellectual property or even altering data to cause poor decision-making
And the list goes on…
The issues surrounding robotics cybersecurity are compounded by the fact that most internal IT teams are already struggling to protect standard systems in their organizations, like computers, telephony, and physical facilities, let alone production and material handling robots. Many do not have the expertise to even address potential cyber threats to industrial robots.
Robot Cybersecurity Challenges with Remote-Control Technologies
As innovations continue in the robotics industries, manufacturing teams are noticing the emergence of remote-control technologies to manage industrial robots and cobots from a distance. These remote-control technologies offer a wide range of benefits, including:
agility in controlling the equipment,
simplifying maintenance,
boosting production efficiency,
cost reductions in technical support and travel fees,
real-time data to determine and fix any issues with the robots.
Nevertheless, manufacturers are concerned about the associated robotics security risks as remote-control technologies most often operate with Internet connections to enable real-time data collection and off-site robot management capabilities.
Indeed, some remote-control technologies can cause cybersecurity issues in robotics. Here are some of the most common problems in industrial robot cybersecurity.
1) Unauthorized Access To The Robot
Malicious criminals or disgruntled employees can use remote-control technologies for robots by altering a robot program without anyone’s knowledge. Some employees may inadvertently tamper with the program. All of this can result in collisions and production stops. Even the smallest changes to a robot’s joint positions, for example, can jeopardize product quality and cause major financial, operational, and legal headaches downstream.
2) Access To Confidential And Proprietary Data
Remote-control technologies in robotics offer a means to control a robot through a company’s computer or tablet that is connected to the Internet. Cybercriminals or competitors could actually leverage the “open access” to the robot to get to the computer and find a wealth of confidential and proprietary data, such as product designs, financial information, access codes, passwords, etc. One can just imagine the amount of harm that can be caused to a business if this type of data is acquired by people with vicious intent.
3) Remote Control Safety When Jogging The Robot
Still, other cybersecurity issues with robots can occur when someone accesses an industrial robot to cause either injury to workers or damage to both the robot itself and surrounding equipment. In these cases, worker safety is compromised, and legal and financial consequences are likely.
Robot Cybersecurity Standards for the Manufacturing Industry
As industrial robots and remote-control monitoring technologies rely on multi-layered and multi-dimensional architecture, new cybersecurity standards are beginning to emerge. Experts in robotics cybersecurity, product manufacturers, integrators, and IT specialists are coming together to develop cybersecurity standards.
These standards are the foundation for both offensive and defensive approaches to cybersecurity for industrial robots. Extensive tests and simulations—not just to the industrial robot itself but to the entire ecosystem a cybercriminal could try to attack, such as the robot enclosure, hardware, user and network interfaces, and mobile applications. Any device or software that communicates with an industrial robot or is housed on a business’ network should be subject to cybersecurity assessments and standards.
How Olis Robotics Makes Robot Remote Control Secure for Manufacturers
Olis Robotics is an innovative company that develops remote monitoring and control technologies for industrial robots. Olis Connect is a plug-and-play solution for remote error recovery of industrial robots. Users can access Universal Robots, Fanuc & ABB robots equipment, and its data directly in a browser.
In order to mitigate the cybersecurity risks that can arise due to remote-control technologies for industrial robots, Olis Robotics has designed several ingenious features and options.
1) Edge-hosted Remote Access Technology
Olis Connect is a edge-hosted solution.
Many new technologies are hosted in the cloud for remote access to industrial robots. However, thanks to Olis, a manufacturer can implement a locally hosted device, also known as edge-hosting.
Contrary to cloud-connected devices, edge-hosted devices can transmit data between local networks. Edge-hosted devices give more flexibility and options for access methods. No Internet connection is required. Once the local device is installed, you can connect it to the local network of the company and access the data/software through a web browser.
2) Flexible Options For Encrypted Internet Access
Olis provides edge-hosted solutions for robot remote access because it gives 100% control over how it gives access to data. Manufacturers can:
Use their existing corporate VPN tunnel
Procure off-the-shelf remote access routes, such as HMS Networks or IXION Cloud
Use Olis’ built-in support for Tailscale, which is a plug-and-play software solution for smaller operations
3) Simple Temporary Access Schemes
Most of the aforementioned solutions can handle temporary access schemes whereby outside access can be given on a time-limited basis when needed.
In certain plants, there might be a desire to have the remote access/control capability available but not enabled by default. In these cases, management can add restrictions, such as key switches, that restrict network access. if downtime occurs and remote expertise is required, access can be turned on within minutes.
4) Remote Control Safety When Jogging The Robot
Olis also has an interesting perspective on ensuring safety when remote “jogging” industrial or collaborative robots.
In the case of traditional robots, it is important to remember that all the safety features of the robot cell still apply, like emergency stops, light curtains, etc. If a worker is in the cell, nobody can remotely control the robot. The safety features “override” any remote-control capabilities.
With collaborative robots, the robot controller has natively integrated safety features. This means that controlling the cobot remotely can be done and certified in a safe and restricted manner.
Safety questions are normal whenever a disruptive technology enters the market; here, Olis Robotics brings this new capability which to be easily able to control industrial robots remotely. However, this capability doesn’t interfere with all the safety features and recommendations already in place.
Key Takeaways
Robotics and cybersecurity make up a complex frontier that manufacturers are just beginning
to explore and understand the nuances. Robots and remote-control technologies offer many benefits that should outweigh the features of a cyberattack. Choosing solutions like Olis Connect and working with experts to implement cybersecurity best practices are two means to safeguard a business from cyberattacks.
FAQs
-
Robots cause cybersecurity issues because they can be connected to IoT networks and the Internet with remote-control technologies.
The Internet is rife with possibilities for cybercriminals to hack a business and its industrial equipment, including robots. Malicious people use the Internet to try to take over a robot or use the robot’s access to internal computers to steal Information.
-
Cybersecurity in robotics is a field that enables businesses to implement measures to safeguard equipment and information from cyberattacks. Cybersecurity in robotics can include processes, standards, programming, IT, and physical infrastructure that prevents or mitigates cyber threats.
As more manufacturers deploy connected robots and cobots in their plants, cybersecurity is becoming a hot topic in robotics.
-
Technologies that enable manufacturers to monitor and control industrial robots/cobots remotely in real-time need the Internet. There is no other way off-site users could control or monitor robots.
However, for manufacturers concerned with cybersecurity issues, there are ways to access a robot with a more localized setup and without using the Internet like the edge-hosted solution from Olis Robotics.